Signs & Symptoms
Causes and Symptoms of Bipolar Mania
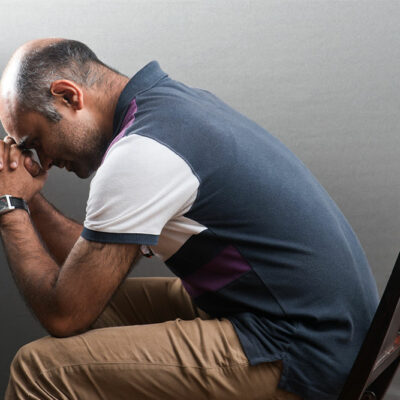
Formerly known as manic depression, bipolar disorder refers to a mental health condition wherein the patients have extreme moods swings, from emotional highs (bipolar mania/hypomania) to emotional lows (depression), with such mood swings occurring multiple times a year. Such mood swings (which are symptoms of bipolar disorder) tend to affect the patient’s ability to think clearly, perform daily activities, and exercise good judgment. It is typically diagnosed in the teenage years or early twenties. However, these bipolar mania symptoms can continue throughout the patient’s life. In bipolar mania, a person tends to demonstrate extreme behavior, particularly an abnormally good mood, strong bursts of energy, hyperactivity, and strongly increased creativity or aggression. The bipolar mania symptoms manifest differently in different people and can last for anywhere from days to a week. Sometimes, attacks might last as long as a few months; usually, they require hospitalization or medication to be kept in check. Manic episodes are often interspersed with periods of depression where the person suffers from exhaustion, hopelessness, and sadness, in other words, the opposite of mania. These are also strong symptoms to watch out for. Bipolar patients may also experience hypomania, which is a milder form of mania and, generally, a more manageable symptom.