Everything You Should Know about a Blood Glucose Test
A blood glucose test is required to measure the amount of glucose (sugar) present in the blood. This is an important aspect of diabetes care since the disease essentially hampers the proper absorption of blood sugar by the body. Let’s look at some of the fundamental aspects of a blood sugar test:
Blood glucose
Glucose is a simple form of sugar that is present in blood in the form of blood sugar.
It is a vital source of energy in microorganisms like bacteria, plants and animals as well as in humans, in different forms. In humans, it enables the working of all the major organs like the brain, heart, liver, kidneys, etc. by providing them with the necessary fuel. Glucose is essential for the functioning of the brain and lower than normal glucose level affects the mental and psychological functions. It can also be stored in the body to be used when required.
Sources of glucose
Energy is released by the conversion of carbohydrates in our food into glucose. However, our food is a combination of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. All the carbohydrates we consume are immediately released into the bloodstream. Some of the proteins are converted into glucose and is stored in the liver for use later. Only very a very small quantity (less than 10%) of fats are converted into glucose and they are absorbed very slowly into the bloodstream.
However, a diet high in fats results in the slower conversion of carbohydrates into glucose. That’s why many people who eat a high-fat diet may find their blood sugar levels spiking after several hours.
Why is high blood sugar harmful?
While glucose is vital for energy, hyperglycemia (excessive levels of blood glucose) or long-term presence of excess sugar in the blood can cause serious damage throughout the body. It can destroy the blood vessels that transport blood to important organs, causing heart problems, strokes, kidney damage, vision problems, nerve damage etc.
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas and it enables regulation of glucose in the bloodstream. When we consume food, signals are sent to the insulin cells which begin to produce insulin. Insulin sends signals to blood cells to allow glucose to enter them and either uses it as fuel or store them for later. Blood sugar levels begin to drop during this process as the glucose is used by the body’s cells. The cells in the pancreas then get the signal to slow down insulin production. This balances the amount of glucose in the blood. In the absence of insulin, or the inability of the body to respond to insulin, all the glucose produced by digestion enters the blood and causes damage.
Blood glucose test
This is a procedure to measure the amount of glucose in your bloodstream. Glucose in the blood is measured in units of millimoles per liter. It may also be measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Blood glucose tends to fluctuate through the day because of the insulin-regulating mechanism.
However, when you have a condition like diabetes, this regulation doesn’t take place and the blood glucose levels remain constantly high. Low blood glucose is equally harmful. It can cause delirium, seizures, brain damage, coma, unconsciousness and even death due to insulin shock.
What are normal levels of glucose in the blood?
- For those below 59, with no other health conditions, between 80-120 mg/dL
- For those above 60, or those who have health conditions like heart disease, lung/kidney disease or low sensitivity to low blood sugar, between 100-140 mg/dL
Testing procedure
Based on your condition, your doctor will recommend testing schedules. Blood glucose can be tested in a lab or at home. There are several different tests:
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test: This test gives you your blood sugar level at a single point in time without your having consumed any food for at least eight hours.
- A1C test: This is a long-term test that monitors blood glucose over three months.
- Random plasma glucose (RPG) test : This is also a single point in time test, but without fasting.
- Other tests for gestational diabetes include glucose challenge test, oral glucose tolerance test, etc
Laboratory testing
In the lab, a small amount of blood is drawn from a vein. This is because arterial blood has the highest concentration of glucose and so it’s advisable to test venous blood to get an accurate level.
Reagents and enzymes like glucose oxidase are used to determine the amount of glucose present in the sample. This method is prescribed by physicians and gives very accurate results. It can be used to diagnose diabetes and hypoglycemia. The blood glucose test is conducted by qualified lab technicians.
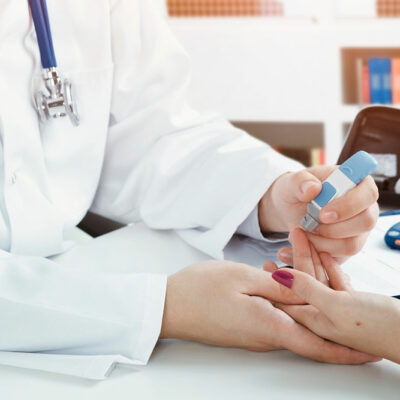
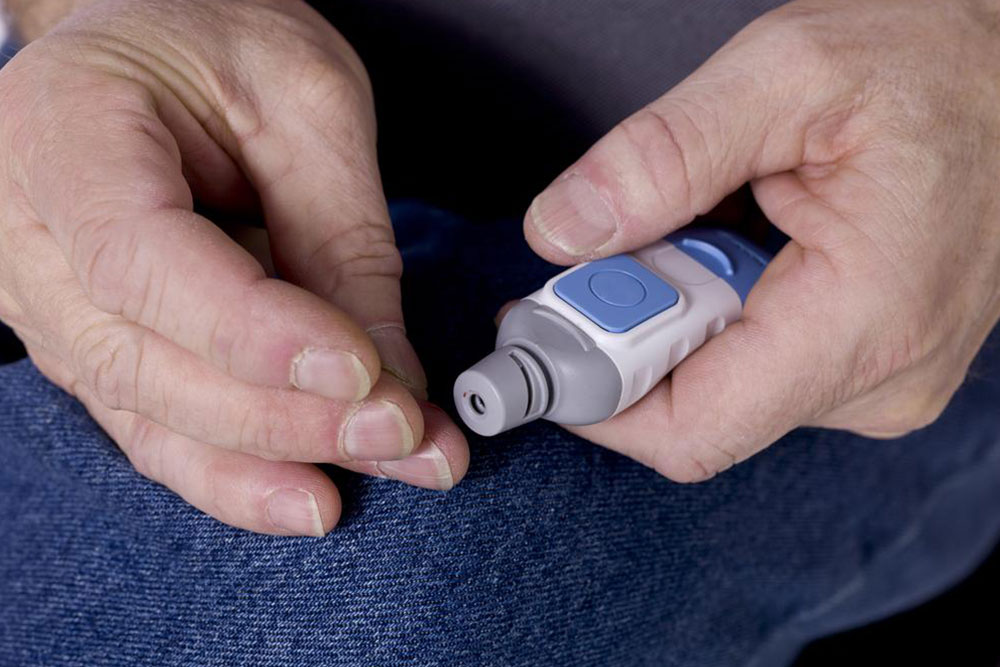
Home testing
The testing procedure requires the use of a testing device called a glucometer. The tip of the finger is pricked to release a drop of blood which is placed on a testing strip. Within a minute the result is displayed on the attached LED screen. This blood glucose test is ideal for home-based self-monitoring by diabetic patients and caregivers.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucose
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_sugar_level
https://www.healthline.com/health/blood-sugar-tests#procedure
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/tests-diagnosis
http://vlab.amrita.edu/?sub=3&brch=63&sim=1343&cnt=1
https://www.healthline.com/health/glucose-test-blood#preparation



